Search Engine¶
Goal¶
The Search class aims to provide a multi-criteria Search engine for GLPI Itemtypes.
It includes some short-cuts functions:
show(): displays the complete search page.showGenericSearch(): displays only the multi-criteria form.showList(): displays only the resulting list.getDatas(): return an array of raw data.manageParams(): complete the$_GETvalues with the$_SESSIONvalues.
The show function parse the $_GET values (calling manageParams()) passed by the page to retrieve the criteria and construct the SQL query.
For showList function, parameters can be passed in the second argument.
The itemtype classes can define a set of search options to configure which columns could be queried, how they can be accessed and displayed, etc..
Todo
datafields option
difference between searchunit and delay_unit
dropdown translations
giveItem
export
fulltext search
Examples¶
To display the search engine with its default options (criteria form, pager, list):
<?php
$itemtype = 'Computer';
Search::show($itemtype);
If you want to display only the multi-criteria form (with some additional options):
<?php
$itemtype = 'Computer';
$p = [
'addhidden' => [ // some hidden inputs added to the criteria form
'hidden_input' => 'OK'
],
'actionname' => 'preview', //change the submit button name
'actionvalue' => __('Preview'), //change the submit button label
];
Search::showGenericSearch($itemtype, $p);
If you want to display only a list without the criteria form:
<?php
// display a list of users with entity = 'Root entity'
$itemtype = 'User';
$p = [
'start' => 0, // start with first item (index 0)
'is_deleted' => 0, // item is not deleted
'sort' => 1, // sort by name
'order' => 'DESC' // sort direction
'reset' => 'reset',// reset search flag
'criteria' => [
[
'field' => 80, // field index in search options
'searchtype' => 'equals', // type of search
'value' => 0, // value to search
],
],
];
Search::showList($itemtype, $p);
GET Parameters¶
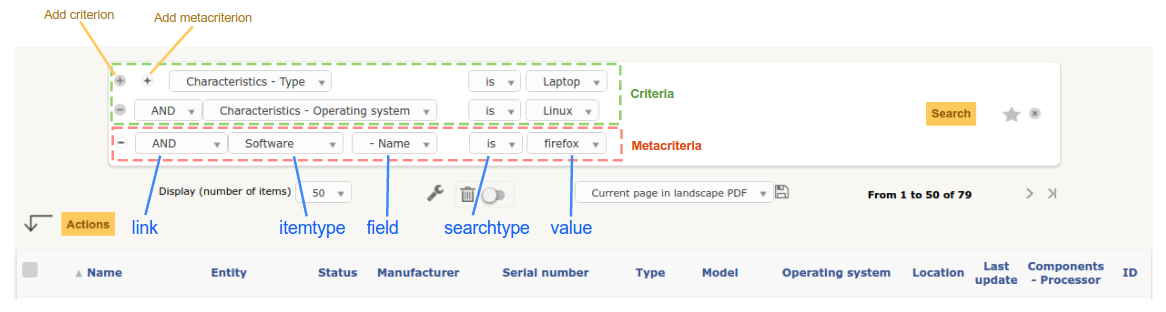
Note
GLPI saves in $_SESSION['glpisearch'][$itemtype] the last set of parameters for the current itemtype for each search query. It is automatically restored on a new search if no reset, criteria or metacriteria is defined.
Here is the list of possible keys which could be passed to control the search engine.
All are optionals.
criteriaAn multi-dimensional array of criterion to filter the search. Each criterion array must provide:
link: one of AND, OR, AND NOT or OR NOT logical operators, optional for first element,field: id of the searchoption,searchtype: type of search, one of:containsequalsnotequalslessthanmorethanundernotunder
value: the value to search
Note
In order to find the field id you want, you may take a look at the getsearchoptions.php tool script.
metacriteriaVery similar to criteria parameter but permits to search in the search options of an itemtype linked to the current (the software of a computer, for example).
Not all itemtype can be linked, see the
getMetaItemtypeAvailable()method of theSearchclass to know which ones could be.The parameter need the same keys as criteria plus one additional:
itemtype: second itemtype to link.
sortid of the searchoption to sort by.
orderEither
ASCfor ending sorting orDESCfor ending sorting.startAn integer to indicate the start point of pagination (SQL
OFFSET).is_deletedA boolean for display trash-bin.
resetA boolean to reset saved search parameters, see note below.
Search options¶
Each itemtype can define a set of options to represent the columns which can be queried/displayed by the search engine. Each option is identified by an unique integer (we must avoid conflict).
Changed in version 9.2: Searchoptions array has been completely rewritten; mainly to catch duplicates and add a unit test to prevent future issues.
To permit the use of both old and new syntax; a new method has been created, getSearchOptionsNew(). Old syntax is still valid (but do not permit to catch duplicates).
The format has changed, but not the possible options and their values!
<?php
function getSearchOptionsNew() {
$tab = [];
$tab[] = [
'id' => 'common',
'name' => __('Characteristics')
];
$tab[] = [
'id' => '1',
'table' => self::getTable(),
'field' => 'name',
'name' => __('Name'),
'datatype' => 'itemlink',
'massiveaction' => false
];
...
return $tab;
}
Note
For reference, the old way to write the same search options was:
<?php
function getSearchOptions() {
$tab = array();
$tab['common'] = __('Characteristics');
$tab[1]['table'] = self::getTable();
$tab[1]['field'] = 'name';
$tab[1]['name'] = __('Name');
$tab[1]['datatype'] = 'itemlink';
$tab[1]['massiveaction'] = false;
...
return $tab;
}
Each option must define the following keys:
tableThe SQL table where the
fieldkey can be found.fieldThe SQL column to query.
nameA label used to display the search option in the search pages (like header for example).
Optionally, it can defined the following keys:
linkfieldForeign key used to join to the current itemtype table.
If not empty, standard massive action (update feature) for this search option will be impossible
searchtype
A string or an array containing forced search type:
equals(may force use of field instead of id when addingsearchequalsonfieldoption)
contains
forcegroupbyA boolean to force group by on this search option
splititemsUse
<hr>instead of<br>to split grouped itemsusehavingUse
HAVINGSQL clause instead ofWHEREin SQL querymassiveactionSet to false to disable the massive actions for this search option.
nosortSet to true to disable sorting with this search option.
nosearchSet to true to disable searching in this search option.
nodisplaySet to true to disable displaying this search option.
joinparamsDefines how the SQL join must be done. See paragraph on joinparams below.
additionalfieldsAn array for additional fields to add in the
SELECTclause. For example:'additionalfields' => ['id', 'content', 'status']datatypeDefine how the search option will be displayed and if a control need to be used for modification (ex: datepicker for date) and affect the searchtype dropdown.
optional parameters are added to the base array of the search option to control more exactly the datatype.See the datatype paragraph below.
Join parameters¶
To define join parameters, you can use one or more of the following:
beforejoin
Define which tables must be joined to access the field.
The array contains
tablekey and may contain an additionaljoinparams.
In case of nestedbeforejoin, we start the SQL join from the last dimension.Example:
<?php [ 'beforejoin' => [ 'table' => 'mytable', 'joinparams' => [ 'beforejoin' => [...] ] ] ]
jointype
Define the join type:
emptyfor a standard jointype::REFTABLE.`#linkfield#` = NEWTABLE.`id`
childfor a child table::REFTABLE.`id` = NEWTABLE.`#linkfield#`
itemtype_itemfor links usingitemtypeanditems_idfields in new table::REFTABLE.`id` = NEWTABLE.`items_id` AND NEWTABLE.`itemtype` = '#ref_table_itemtype#'
itemtype_item_revert(since 9.2.1) for links usingitemtypeanditems_idfields in ref table::NEWTABLE.`id` = REFTABLE.`items_id` AND REFTABLE.`itemtype` = '#new_table_itemtype#'
mainitemtype_mainitemsame asitemtype_itembut using mainitemtype and mainitems_id fields::REFTABLE.`id` = NEWTABLE.`mainitems_id` AND NEWTABLE.`mainitemtype` = 'new table itemtype'
itemtypeonlysame asitemtype_itemjointype but without linking id::NEWTABLE.`itemtype` = '#new_table_itemtype#'
item_itemfor table used to link two similar items:glpi_tickets_ticketsfor example: link fields arestandardfk_1andstandardfk_2::REFTABLE.`id` = NEWTABLE.`#fk_for_new_table#_1` OR REFTABLE.`id` = NEWTABLE.`#fk_for_new_table#_2`
item_item_revertsame asitem_itemand child jointypes::NEWTABLE.`id` = REFTABLE.`#fk_for_new_table#_1` OR NEWTABLE.`id` = REFTABLE.`#fk_for_new_table#_2`
condition
Additional condition to add to the standard link.
Use
NEWTABLEorREFTABLEtag to use the table names.Changed in version 9.4.
An array of parameters used to build a WHERE clause from GLPI querying facilities. Was previously only a string.
nolink
Set to true to indicate the current join does not link to the previous join/from (nested
joinparams)
Data types¶
Available datatypes for search are:
date
Available parameters (all optional):
searchunit: one of MySQL DATE_ADD unit, default toMONTH
maybefuture: display datepicker with future date selection, defaults tofalse
emptylabel: string to display in case ofnullvalue
datetime
Available parameters (all optional) are the same as
date.
date_delay
Date with a delay in month (
end_warranty,end_date).Available parameters (all optional) are the same as
dateand:
datafields: array of data fields that would be used.
datafields[1]: the date field,
datafields[2]: the delay field,
datafields[2]: ?
delay_unit: one of MySQL DATE_ADD unit, default toMONTH
timestamp
Use
Dropdown::showTimeStamp()for modificationAvailable parameters (all optional):
withseconds: boolean (falseby default)
weblink
Any URL
email
Any email address
color
Use
Html::showColorField()for modification
text
Use text area input for modification (optionally rich-text)
string
Simple, single-line text
ip
Any IP address
mac
Available parameters (all optional):
htmltext: boolean, escape the value (falseby default)
number
Use a
Dropdown::showNumber()for modification (in case ofequalssearchtype).
Forcontainssearchtype, you can use < and > prefix invalue.Available parameters (all optional):
width: html attribute passed to Dropdown::showNumber()
min: minimum value (default0)
max: maximum value (default100)
step: step for select (default1)
toadd: array of values to add a the beginning of the dropdown
integer
Alias for
number
count
Same as
numberbut count the number of item in the table
decimal
Same as
numberbut formatted with decimal
bool
Use
Dropdown::showYesNo()for modification
itemlink
Create a link to the item
itemtypename
Use
Dropdown::showItemTypes()for modificationAvailable parameters (all optional) to define available itemtypes:
itemtype_list: one of $CFG_GLPI[“unicity_types”]
types: array containing available types
language
Use
Dropdown::showLanguages()for modificationAvailable parameters (all optional):
display_emptychoice: display an empty choice (-------)
right
Use
Profile::dropdownRights()for modificationAvailable parameters (all optional):
nonone: hide none choice ? (defaults tofalse)
noread: hide read choice ? (defaults tofalse)
nowrite: hide write choice ? (defaults tofalse)
dropdown
Use
Itemtype::dropdown()for modification.
Dropdown may have several additional parameters depending of dropdown type :rightfor user one for example
specific
If not any of the previous options matches the way you want to display your field, you can use this datatype.
See specific search options paragraph for implementation.
Specific search options¶
You may want to control how to select and display your field in a searchoption.
You need to set ‘datatype’ => ‘specific’ in your search option and declare these methods in your class:
getSpecificValueToDisplayDefine how to display the field in the list.
Parameters:
$field: column name, it matches the ‘field’ key of your searchoptions$values: all the values of the current row (for select)$options: will contains these keys:html,searchopt: the current full searchoption
getSpecificValueToSelect
Define how to display the field input in the criteria form and massive action.
Parameters:
$field: column name, it matches the ‘field’ key of your searchoptions
$values: the current criteria value passed in $_GET parameters
$name: the html attribute name for the input to display
$options: this array may vary strongly in function of the searchoption or from the massiveaction or criteria display. Check the corresponding files:
Simplified example extracted from CommonItilObject Class for glpi_tickets.status field:
<?php
function getSearchOptionsMain() {
$tab = [];
...
$tab[] = [
'id' => '12',
'table' => $this->getTable(),
'field' => 'status',
'name' => __('Status'),
'searchtype' => 'equals',
'datatype' => 'specific'
];
...
return $tab;
}
static function getSpecificValueToDisplay($field, $values, array $options=array()) {
if (!is_array($values)) {
$values = array($field => $values);
}
switch ($field) {
case 'status':
return self::getStatus($values[$field]);
...
}
return parent::getSpecificValueToDisplay($field, $values, $options);
}
static function getSpecificValueToSelect($field, $name='', $values='', array $options=array()) {
if (!is_array($values)) {
$values = array($field => $values);
}
$options['display'] = false;
switch ($field) {
case 'status' :
$options['name'] = $name;
$options['value'] = $values[$field];
return self::dropdownStatus($options);
...
}
return parent::getSpecificValueToSelect($field, $name, $values, $options);
}
Default Select/Where/Join¶
The search class implements three methods which add some stuff to SQL queries before the searchoptions computation.
For some itemtype, we need to filter the query or additional fields to it.
For example, filtering the tickets you cannot view if you do not have the proper rights.
GLPI will automatically call predefined methods you can rely on from your plugin hook.php file.
addDefaultSelect¶
See addDefaultSelect() method documentation
And in the plugin hook.php file:
<?php
function plugin_mypluginname_addDefaultSelect($itemtype) {
switch ($type) {
case 'MyItemtype':
return "`mytable`.`myfield` = 'myvalue' AS MYNAME, ";
}
return '';
}
addDefaultWhere¶
See addDefaultWhere() method documentation
And in the plugin hook.php file:
<?php
function plugin_mypluginname_addDefaultJoin($itemtype, $ref_table, &$already_link_tables) {
switch ($itemtype) {
case 'MyItemtype':
return Search::addLeftJoin(
$itemtype,
$ref_table,
$already_link_tables,
'newtable',
'linkfield'
);
}
return '';
}
addDefaultJoin¶
See addDefaultJoin()
And in the plugin hook.php file:
<?php
function plugin_mypluginname_addDefaultWhere($itemtype) {
switch ($itemtype) {
case 'MyItemtype':
return " `mytable`.`myfield` = 'myvalue' ";
}
return '';
}
Bookmarks¶
The glpi_bookmarks table stores a list of search queries for the users and permit to retrieve them.
The query field contains an url query construct from parameters with http_build_query PHP function.
Display Preferences¶
The glpi_displaypreferences table stores the list of default columns which need to be displayed to a user for an itemtype.
A set of preferences can be personal or global (users_id = 0).
If a user does not have any personal preferences for an itemtype, the search engine will use the global preferences.
